Posts Tagged ‘Product Design’
Product Design – the most powerful (and missing) element of lean
Lean has been beneficial for many companies, helping improve competitiveness and profitability. But, lean has not been nearly as effective as it can be because there is a missing ingredient – product design. Where lean can reduce the waste of making and moving parts, product design can eliminate the parts altogether; where lean can reduce setup times for big machines, product design can change the parts so they no longer need the big machines; where lean can reduce inventory, product design can eliminate it by designing out parts; where lean can make the supply chain more efficient, product design can radically shorten it by designing out the long lead time elements.
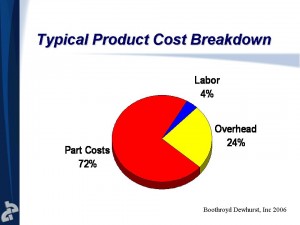
The power of product design is even more evident when considering the breakdown of product cost. Here is some data from Nick Dewhurst taken from multiple-hundred DFMA analyses showing the typical cost breakdown of products.
Of the three buckets of cost, material cost is by far the largest 74%, and this is where product development shines. Product design can eliminate 40 to 50% of material cost resulting in radical cost savings. Lean cannot. I will go a bit further and say that material cost reductions are largely off limits to the lean folks since it requires fundamental product changes.
Side note – Probably most surprising about cost breakdown data is labor cost is only 4%. Why we move our manufacturing to “low cost countires” to chase 50% labor reductions to net a whopping 2% cost reduction is beyond me, but that’s for a different post.
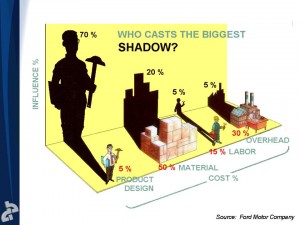
Let’s face it – material cost reduction is where it’s at, and lean does not have the toolbox to reduce material cost. There’s no mystery here. What is mysterious, however, is that companies looking to survive at all costs are not pulling the biggest lever at their disposal – product design. Here is a bit of old data from Ford showing that Product Design has the biggest lever on cost. We’ve know this for a long time, but we still don’t do it.
Clearly, the best approach of is to combine the power of product design with lean. It goes like this: the engineers design a low cost, low waste product that is introduced to the production line, and the lean folks improve efficiency and reduce cost from there. We’ve got the lean part down, but not the product design part.
There are two things in the way of designing low cost, low waste products in a way that helps take lean to the next level. First, product development teams don’t know how to do the work. To overcome this, train them in DFMA. Second, and most important, company leaders don’t give the product development teams the tools, time, and training to do the work. Company leaders won’t take the time to do the work because they think it will delay product launches. Also, they don’t want to invest in the tools and training because the cost is too high, even though a little math shows the investment is more than paid back with the first product launch. To fix that, educate them on the methods, the resource needs, and the savings.
Good luck.
Engineering your way out of the recession
 Like you, I have been thinking a lot about the recession. We all want to know how to move ourselves to the other side, where things are somewhat normal (the old normal, not the new one). Like usual, my mind immediately goes to products. To me, having the right products is vital to pulling ourselves out of this thing. There is nothing novel in this thinking; I think we all agree that products are important. But, there are two follow-on questions that are important. First, what makes products “right” to move you quickly to the other side? Second, do you have the capability to engineer the “right” products?
Like you, I have been thinking a lot about the recession. We all want to know how to move ourselves to the other side, where things are somewhat normal (the old normal, not the new one). Like usual, my mind immediately goes to products. To me, having the right products is vital to pulling ourselves out of this thing. There is nothing novel in this thinking; I think we all agree that products are important. But, there are two follow-on questions that are important. First, what makes products “right” to move you quickly to the other side? Second, do you have the capability to engineer the “right” products?
The first question – what makes products “right” for these times? Capacity is important to understanding what makes products right. Capacity utilization is at record lows with most industries suffering from a significant capacity glut. With decreased sales and idle machines, customers are no longer interested in products that improve productivity of their existing product lines because they can simply run their idle machines more. And, they are not interested in buying more capacity (your products) at a reduced price. They will simply run their idle machines more. You can’t offer an improvement of your same old product that enables customers to make their same old products a bit faster and you can’t offer them your same old products at a lower price. However, you can sell them products that enable them to capture business they currently do not have. For example, enable them to manufacture products that their idle machines CANNOT make at all. To do that means your new products must do something radically different than before; they must have radically improved functionality or radically new features. This is what makes products right for these times.
On to the second question – do you have the capability to engineer the right products? Read the rest of this entry »
Part Cutters – Design for assembly dramatically reduces complexity of plasma arc cutter, Joseph Ogando, Senior Editor, Design News
The engineers at Hypertherm Inc., a maker of plasma cutting systems,know a thing or two about cutting metals. They also know how to cut cost. A lot of cost. While redesigning one of the company’s best-selling plasma cutting systems, they managed to reduce parts’ count from more than 1,000 components to fewer than 500. System assembly time fell from 20 hours to less than five. And the output from the company’s existing assembly operation quadrupled — without any additional floor space or an expensive second shift. Bottom line: the redesign saved the company about $5 million in assembly costs over the past 24 months alone, according to Engineering Manager Mike Shipulski. Read the rest of this entry »
Redesigns get radical improvements using DFMA
Redesigns get radical improvements using DFMA
Hypertherm, Inc. of Hanover, NH, is among the world’s foremost manufacturers of plasma arc cutting equipment. Founded in 1968 with a staff of two, the company today has 750 employees, with subsidiaries, sales offices, and distributors in multiple countries. All technology development, product development, and manufacturing is done in the Hanover area.

View of the new HyPerformance Plasma HPR130 plasma cutter from Hypertherm. The company used Design for Manufacture and Analysis (DFMA) methodology to radically redesign — and improve — the system’s manufacturability. In the new plasma cutter, system subassemblies took 45% to 89% less time to put together. Assembly floor space opened up by 40%. Warranty cost went down 83%. Cost savings amounted to $5 million over 24 months, which helped the company achieve record earnings and its highest profit sharing on record.
Hypertherm’s products range from lightweight, manual plasma cutting equipment to highly mechanized systems that operate with CNC cutting machines. Its advanced technology serves a global customer base in every industry that depends on quality and reliability in high-temperature metal cutting, such as shipbuilding, construction, farm equipment, rail car and truck manufacture, and plant maintenance.
Recently, Hypertherm engineers tackled a project of mammoth proportions when they remodeled the company’s highly successful HD3070 plasma cutting system — and ultimately created the new HyPerformance Plasma HPR130 plasma cutter. Before the redesign project, the HD3070 sold well and was widely regarded as a standard for robust, high-precision cutting in the industry. Hypertherm wanted to make the product even better.
“We started with a vision to make a radical improvement in product performance coupled with a radical reduction in product cost,” says Mike Shipulski, director of engineering for Hypertherm. He believed that using the methodology of Design for Manufacture and Analysis (DFMA) would help identify unnecessary parts, highlight assembly difficulties that Read the rest of this entry »
 Mike Shipulski
Mike Shipulski