Archive for the ‘Fear’ Category
The Power of Stopping
 If when you write your monthly report no one responds with a question of clarification or constructive comment, this may be a sign your organization places little value on your report and the work it stands for. If someone sends a thank you email and do not mention something specific in your report, this masked disinterest is a half-step above non-interest and is likely also a sign your organization places little value on your report and the work it stands for.
If when you write your monthly report no one responds with a question of clarification or constructive comment, this may be a sign your organization places little value on your report and the work it stands for. If someone sends a thank you email and do not mention something specific in your report, this masked disinterest is a half-step above non-interest and is likely also a sign your organization places little value on your report and the work it stands for.
If you want to know for sure what people think of your work, stop writing your report. If no one complains, your work is not valuable to the company. If one person complains, it’s likely still not valuable. And if that single complaint comes from your boss, your report/work is likely not broadly valuable, but you’ll have to keep writing the report.
But don’t blame the organization because they don’t value your work. Instead, ask yourself how your work must change so it’s broadly valuable. And if you can’t figure a way to make your work valuable, stop the work so you can start work that is.
If when you receive someone else’s monthly report and you don’t reply with a question of clarification or constructive comment, it’s because you don’t think their work is all that important. And if this is the case, tell them you want to stop receiving their report and ask them to stop sending them to you. Hopefully, this will start a discussion about why you want to stop hearing about their work which, hopefully, will lead to a discussion about how their work could be modified to make it more interesting and important. This dialog will go one of two ways – they will get angry and take you off the distribution list or they will think about your feedback and try to make their work more interesting and important. In the first case, you’ll receive one fewer report and in the other, there’s a chance their work will blossom into something magical. Either way, it’s a win.
While reports aren’t the work, they do stand for the work. And while reports are sometimes considered overhead, they do perform an inform function – to inform the company of the work that’s being worked. If the work is amazing, the reports will be amazing and you’ll get feedback that’s amazing. And if the work is spectacular, the reports will be spectacular and you’ll get feedback that matches.
But this post isn’t about work or reports, it’s about the power of stopping. When something stops, the stopping is undeniable and it forces a discussion about why the stopping started. With stopping, there can be no illusion that progress is being made because stopping is binary – it’s either stopped or it isn’t. And when everyone knows progress is stopped, everyone also knows the situation is about to get some much-needed attention from above, wanted or not.
Stopping makes a statement. Stopping gets attention. Stopping is serious business.
And here’s a little-known fact: Starting starts with stopping.
Image credit — joiseyshowaa
What you do next is up to you.
 If you don’t know why you’re doing what you’re doing, you can try to remember why you started the whole thing or you can do something else. Either can remedy things, but how do you choose between them? If you’ve forgotten your “why”, maybe it’s worth forgetting or maybe something else temporarily came up that pushed your still-important why underground for a short time. If it’s worth forgetting, maybe it’s time for something else. And if it’s worth remembering, maybe it’s time to double down. Only you can choose.
If you don’t know why you’re doing what you’re doing, you can try to remember why you started the whole thing or you can do something else. Either can remedy things, but how do you choose between them? If you’ve forgotten your “why”, maybe it’s worth forgetting or maybe something else temporarily came up that pushed your still-important why underground for a short time. If it’s worth forgetting, maybe it’s time for something else. And if it’s worth remembering, maybe it’s time to double down. Only you can choose.
If you still remember why you’re doing what you’re doing, you can ask yourself if your why is still worth its salt or if something changed, either inside you or in your circumstances, that has twisted your why to something beyond salvage. If your why is still as salty as ever, maybe it’s right to stay the course. But if it’s still as salty as ever but you now think it’s distasteful, maybe it’s time for a change.
When you do what you did last time, are you more efficient or more dissatisfied, or both? And if you imagine yourself doing it again, do you look forward to more efficiency or predict more dissatisfaction? These questions can help you decide whether to keep things as they are or change them.
What have you learned over the last year? Whether your list is long or if it’s short, it’s a good barometer to inform your next chapter.
What new skills have you mastered over the last year? Is the list long or short? If you don’t want to grow your mastery, keep things as they are.
Do the people you work with inspire you or bring you down? Are you energized or depleted by them? If you’re into depletion, there’s no need to change anything.
Do you have more autonomy than last year? And how do you feel about that? Let your answers guide your future.
What is the purpose behind what you do? Is it aligned with your internal compass? These two questions can bring clarity.
You’re the only one who can ask yourself these questions; you’re the only one who can decide if you like the answers; and you’re the only one who is responsible for what you do next. What you do next is up to you.
“Fork in the road” by Kai Hendry is licensed under CC BY 2.0.
Triangulation of Leadership
Put together things that contradict yet make a wonderfully mismatched pair.
Say things that contradict common misunderstandings.
See the dark and dirty underside of things.
Be more patient with people.
Stomp on success.
Dissent.
Tell the truth even when it’s bad for your career.
See what wasn’t but should have been.
Violate first principles.
Protect people.
Trust.
See things as they aren’t.
See what’s missing.
See yourself.
See.
“man in park (triangulation)” by Josh (broma) is licensed under CC BY 2.0.
Do you build trust or break it?
When someone tells you their truth, what do you do? Do you ask them to defend? Do you tell them what you think? Do you dismiss them? Do you listen? Do you believe them?
When someone has the courage to tell you their truth, they demonstrate they trust you. If you want to destroy their trust, ask them to defend their truth. Sooner or later, or then and there, they’ll stop trusting you. And like falling off a cliff, it’s almost impossible for things to be the same.
When someone confesses their truth, they demonstrate they trust you enough to share a difficult issue with you. If you want them to feel small and block them from sharing their truth in the future, tell them why their truth isn’t right. That will be the last time they speak candidly with you. Ever.
When someone reluctantly shares their truth, they demonstrate they’re willing to push through their discomfort due to the significance and their trust in you. If you want them to get angry, explain how they see things incorrectly or tell them what they don’t understand. Either one will cause them to move to a purely transactional relationship with you. And there’s no coming back from that.
When someone confides in you and shares their truth, you ask them to defend it, and, despite your unskillful response they share it again, believe them. And if you don’t, you’ll damn yourself twice.
When someone shares their truth and you listen without judging, you build trust.
When someone sends you a heartfelt email describing a dilemma and your response is to set up a meeting to gain a fuller understanding, you build trust.
When someone demonstrates the courage to share a truth that they know contradicts the mission, believe them. You’ll build trust.
When someone shares their truth, you have an opportunity to build trust or break it. Which will you choose?
Image credit — Christian Scheja
Tell the truth, especially when it’s difficult.
 Our behavior is a result of causes and conditions. One thing paves the way for the next. Elements of the first thing create a preferential path for the next thing. If someone gets praised for doing A, more people will do A, even when A is the wrong behavior. If someone gets chastised for doing B, B won’t happen again, even when B is the right behavior.
Our behavior is a result of causes and conditions. One thing paves the way for the next. Elements of the first thing create a preferential path for the next thing. If someone gets praised for doing A, more people will do A, even when A is the wrong behavior. If someone gets chastised for doing B, B won’t happen again, even when B is the right behavior.
The most troubling set of causes and conditions are those that block people from telling their truth. When everyone knows it’s a bad idea, but no one is willing to say it out loud, that’s a big problem. In fact, it may be the biggest problem.
When people think they won’t be taken seriously, they keep their truth to themselves. When people know they will be dismissed, they keep quiet. When people feel the situation is hopeless because there’s no way they’ll be listened to, they say nothing.
When people see others not taken seriously, that creates conditions for future truths to be withheld. When people see others being dismissed, that creates conditions for future truths to be kept quiet. When people see others in others from not being listened to, that creates conditions for future truths to remain unsaid.
And causes and conditions are self-strengthening. The more causes and conditions are reinforced, the more the behaviors become ingrained. The more people are stifled, the more they will keep quiet. The more people are dismissed, the more they’ll shut up. The more people’s truths are ignored, the more they’ll remain unsaid.
Here are three rules for truth-telling that will help you and your company move forward:
- Without truth-telling, there can be no truth-telling.
- The longer truth-telling is stifled, the harder it is for truth-telling to reemerge.
- Truth-telling begets truth-telling.
Image credit — Jinterwas
When You Don’t Know What To Do…
 When you don’t know what to do, what do you do? This is a difficult question.
When you don’t know what to do, what do you do? This is a difficult question.
Here are some thoughts that may help you figure out what to do when you really don’t know.
Don’t confuse activity with progress.
Gather your two best friends, go off-site, and define the system as it is.
Don’t ask everyone what they think because the Collective’s thoughts will be diffuse, bland, and tired.
Get outside.
Draw a picture of how things work today.
Get a good meal.
Make a graph of goodness over time. If it’s still increasing, do more of what you did last time. If it’s flat, do something else.
Get some exercise.
Don’t judge yourself negatively. This is difficult work.
Get some sleep.
Help someone with their problem. The distraction will keep you out of the way as your mind works on it for you.
Spend time with friends.
Try a new idea at the smallest scale. It will likely lead to a better one. Repeat.
Use your best judgment.
Image credit – Andrew Gustar
Effective Interactions During Difficult Times
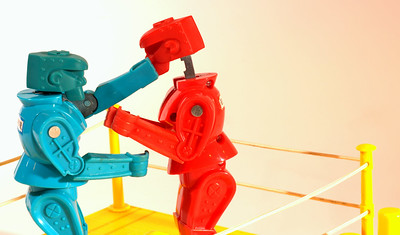 When times are stressful, it’s more difficult to be effective and skillful in our interactions with others. Here are some thoughts that could help.
When times are stressful, it’s more difficult to be effective and skillful in our interactions with others. Here are some thoughts that could help.
Decide how you want to respond, and then respond accordingly.
Before you respond, take a breath. Your response will be better.
If you find yourself responding before giving yourself permission, stop your response and come clean.
Better responses from you make for even better responses from others.
If you interrupt someone in the middle of their sentence so you can make your point, you made a different point.
If you find yourself preparing your response while listening to someone, that’s not listening.
If you recognize you’re not listening, now there are at least two people who know the truth.
When there are no words coming from your mouth, that doesn’t constitute listening.
The strongest deterrent to listening is talking.
If you disagree with one element of a person’s position, you can, at the same time, agree with other elements of their position. That’s how agreement works.
If you start with agreement, even the smallest bit, disagreement softens.
Before you can disagree, it’s important to listen and understand. And it’s the same with agreement.
It’s easy to agree if that’s what you want to accomplish. And it’s the same for disagreement.
If you want to move toward agreement, start with understanding.
If you want to demonstrate understanding, start with listening.
If you want to demonstrate good listening, start with kindness.
Here are three mantras I find helpful:
Talk less to listen more.
Before you respond, take a breath.
Kindness before agreement.
“Rock-em” by REL Waldman is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0
The Two Sides of the Story
 When you tell the truth and someone reacts negatively, their negativity is a surrogate for significance.
When you tell the truth and someone reacts negatively, their negativity is a surrogate for significance.
When you withhold the truth because someone will react negatively, you do everyone a disservice.
When you know what to do, let someone else do it.
When you’re absolutely sure what to do, maybe you’ve been doing it too long.
When you’re in a situation of complete uncertainty, try something. There’s no other way.
When you’re told it’s a bad idea, it’s probably a good one, but for a whole different reason.
When you’re told it’s a good idea, it’s time to come up with a less conventional idea.
When you’re afraid to speak up, your fear is a surrogate for importance.
When you’re afraid to speak up and you don’t, you do your company a disservice.
When you speak up and are met with laughter, congratulations, your idea is novel.
When you get angry, that says nothing about the thing you’re angry about and everything about you.
When someone makes you angry, that someone is always you.
When you’re afraid, be afraid and do it anyway.
When you’re not afraid, try harder.
When you’re understood the first time you bring up a new idea, it’s not new enough.
When you’re misunderstood, you could be onto something. Double down.
When you’re comfortable, stop what you’re doing and do something that makes you uncomfortable.
It’s time to get comfortable with being uncomfortable.
“mirror-image pickup” by jasoneppink is licensed under CC BY 2.0
How To Be Novel
 By definition, the approach that made you successful will become less successful over time and, eventually, will run out of gas. This fundamental is not about you or your approach, rather it’s about the nature of competition and evolution. There’s an energy that causes everything to change, grow and improve and your success attracts that energy. The environment changes, the people change, the law changes and companies come into existence that solve problems in better and more efficient ways. Left unchanged, every successful business endeavor (even yours) has a half-life.
By definition, the approach that made you successful will become less successful over time and, eventually, will run out of gas. This fundamental is not about you or your approach, rather it’s about the nature of competition and evolution. There’s an energy that causes everything to change, grow and improve and your success attracts that energy. The environment changes, the people change, the law changes and companies come into existence that solve problems in better and more efficient ways. Left unchanged, every successful business endeavor (even yours) has a half-life.
If you want to extend the life of your business endeavor, you’ve got to be novel.
By definition, if you want to grow, you’ve got to raise your game. You’ve got to do something different. You can’t change everything, because that’s inefficient and takes too long. So, you’ve got to figure out what you can reuse and what you’ve got to reinvent.
If you want to grow, you’ve got to be novel.
Being novel is necessary, but expensive. And risky. And scary. And that’s why you want to add just a pinch of novelty and reuse the rest. And that’s why you want to try new things in the smallest way possible. And that’s why you want to try things in a time-limited way. And that’s why you want to define what success looks like before you test your novelty.
Some questions and answers about being novel:
Is it easy to be novel? No. It’s scary as hell and takes great emotional strength.
Can anyone be novel? Yes. But you need a good reason or you’ll do what you did last time.
How can I tell if I’m being novel? If you’re not scared, you’re not being novel. If you know how it will turn out, you’re not being novel. If everyone agrees with you, you’re not being novel.
How do I know if I’m being novel in the right way? You cannot. Because it’s novel, it hasn’t been done before, and because it hasn’t been done before there’s no way to predict how it will go.
So, you’re saying I can’t predict the outcome of being novel? Yes.
If I can’t predict the outcome of being novel, why should I even try it? Because if you don’t, your business will go away.
Okay. That last one got my attention. So, how do I go about being novel? It depends.
That’s not a satisfying answer. Can you do better than that? Well, we could meet and talk for an hour. We’d start with understanding your situation as it is, how this current situation came to be, and talk through the constraints you see. Then, we’d talk about why you think things must change. I’d then go away for a couple of days and think about things. We’d then get back together and I’d share my perspective on how I see your situation. Because I’m not a subject matter expert in your field, I would not give you answers, but, rather, I’d share my perspective that you could use to inform your choice on how to be novel.
“Giraffe trying to catch a twig with her tongue” by Tambako the Jaguar is licensed under CC BY-ND 2.0
When you decide you have enough, the right work WILL happen.
 If you are happy with what you have, others have no power over you.
If you are happy with what you have, others have no power over you.
If you don’t want more, you call the shots.
If you have nothing to prove, no one can manipulate you.
If you have enough, the lure of more cannot pull you off the path of what you think is right.
If you don’t need approval from others, you can do what you think is right.
If you know what’s important to you, you can choose the path forward.
If you know who you are, so does everyone else.
If you know who you are, you don’t care what others think of you.
When you don’t care about what others think about you, you can do the right work.
When you can do the right work in the right way, you are impervious to influence.
When you are impervious to influence, the right work happens, despite the displeasure of the Status Quo.
Anne Ruthmann is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
If you want to understand innovation, understand novelty.
 If you want to get innovation right, focus on novelty.
If you want to get innovation right, focus on novelty.
Novelty is the difference between how things are today and how they might be tomorrow. And that comparison calibrates tomorrow’s idea within the context of how things are today. And that makes all the difference. When you can define how something is novel, you have an objective measure of things.
How is it different than what you did last time? If you don’t know, either you don’t know what you did last time or you don’t know the grounding principle of your new idea. Usually, it’s a little of the former and a whole lot of the latter. And if you don’t know how it’s different, you can’t learn how potential customers will react to the novelty. In fact, if you don’t know how it’s different, you can’t even decide who are the right potential customers.
A new idea can be novel in unique ways to different customer segments and it can be novel in opposite ways to intermediaries or other partners in the business model. A customer can see the novelty as something that will make them more profitable and an intermediary can see that same novelty as something that will reduce their influence with the customer and lead to their irrelevance. And, they’ll both be right.
Novelty is in the eye of the beholder, so you better look at it from their perspective.
Like with hot sauce, novelty comes in a range of flavors and heat levels. Some novelty adds a gentle smokey flavor to your favorite meal and makes you smile while the ghost pepper variety singes your palate and causes you to lose interest in the very meal you grew up on. With novelty, there is no singular level of Scoville Heat Unit (SHU) that is best. You’ve got to match the heat with the situation. Is it time to improve things a bit with a smokey, yet subtle, chipotle? Or, is it time to submerge things in pure capsaicin and blow the roof off? The good news is the bad news – it’s your choice.
With novelty, you can choose subtle or spicy. Choose wisely.
And like with hot sauce, novelty doesn’t always mix well with everything else on the plate. At the picnic, when you load your plate with chicken wings, pork ribs, and apple pie, it’s best to keep the hot sauce away from the apple pie. Said more strongly, with novelty, it’s best to use separate plates. Separate the teams – one team to do heavy novelty work, the disruptive work, to obsolete the status quo, and a separate team to the lighter novelty work, the continuous improvement work, to enhance the existing offering.
Like with hot sauce, different people have different tolerance levels for novelty. For a given novelty level, one person can be excited while another can be scared. And both are right. There’s no sense in trying to change a person’s tolerance for novelty, they either like it or they don’t. Instead of trying to teach them to how to enjoy the hottest hot sauce, it’s far more effective to choose people for the project whose tolerance for novelty is in line with the level of novelty required by the project.
Some people like habanero hot sauce, and some don’t. And it’s the same with novelty.


 Mike Shipulski
Mike Shipulski